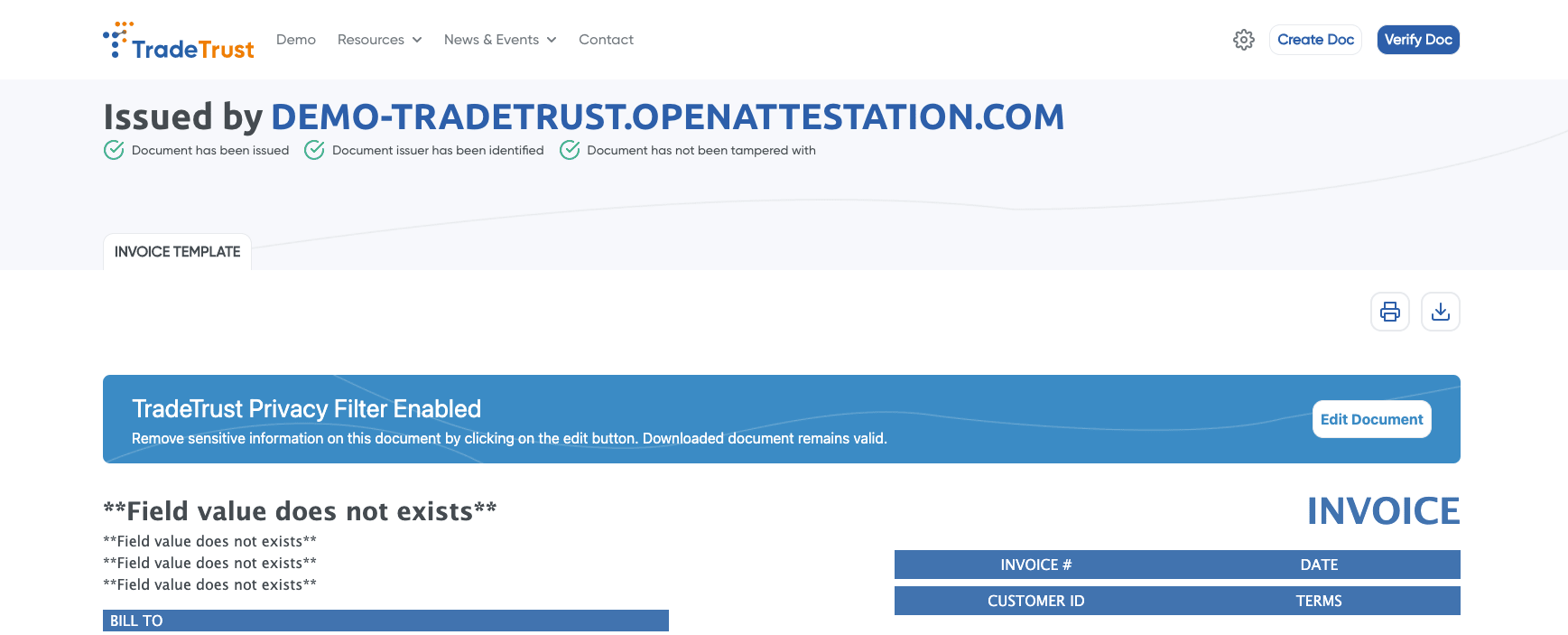
DID sign demo
The following example will show how to sign a DID document with AWS KMS key. (demonstration only)
IMPORTANT: You must be careful on the way you expose the secret key and the access key. Always follow AWS security best practices.
Tutorial
Define some imports first:
require("dotenv").config();
const fs = require("fs");
const {
wrapDocument,
signDocument,
SUPPORTED_SIGNING_ALGORITHM,
} = require("@tradetrust-tt/tradetrust");
const { AwsKmsSigner } = require("ethers-aws-kms-signer");
Prepare the signer by providing the needed parameters gotten from previous steps:
const signer = new AwsKmsSigner({
accessKeyId: <Access key ID>,
secretAccessKey: <Secret access key>,
region: <Region>, // example: ap-southeast-1
keyId: <Key ID>,
});
Prepare an example document (can refer to this) that is to be signed:
const address = await signer.getAddress();
const document = {
recipient: {
name: "John Doe",
},
$template: {
name: "main",
type: "EMBEDDED_RENDERER",
url: "https://tutorial-renderer.openattestation.com",
},
issuers: [
{
id: `did:ethr:${address}`,
name: "Demo Issuer",
revocation: {
type: "NONE",
},
identityProof: {
type: "DID",
key: `did:ethr:${address}#controller`,
},
},
],
};
Then sign the document (make sure to wrap document first):
signDocument(
wrapDocument(document),
SUPPORTED_SIGNING_ALGORITHM.Secp256k1VerificationKey2018,
signer
).then((response) => {
const data = JSON.stringify(response, null, 2);
fs.writeFileSync("./document.json", data);
});
Full code example
// index.js
require("dotenv").config();
const fs = require("fs");
const {
wrapDocument,
signDocument,
SUPPORTED_SIGNING_ALGORITHM,
} = require("@tradetrust-tt/tradetrust");
const { AwsKmsSigner } = require("ethers-aws-kms-signer");
const signer = new AwsKmsSigner({
accessKeyId: process.env.KMS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,
secretAccessKey: process.env.KMS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY,
region: process.env.KMS_REGION,
keyId: process.env.KMS_KEY_ID,
});
const didSignDemo = async () => {
const address = await signer.getAddress();
const document = {
recipient: {
name: "John Doe",
},
$template: {
name: "main",
type: "EMBEDDED_RENDERER",
url: "https://tutorial-renderer.openattestation.com",
},
issuers: [
{
id: `did:ethr:${address}`,
name: "Demo Issuer",
revocation: {
type: "NONE",
},
identityProof: {
type: "DID",
key: `did:ethr:${address}#controller`,
},
},
],
};
signDocument(
wrapDocument(document),
SUPPORTED_SIGNING_ALGORITHM.Secp256k1VerificationKey2018,
signer
).then((response) => {
const data = JSON.stringify(response, null, 2);
fs.writeFileSync("./document.json", data);
console.log(data);
});
};
didSignDemo();
// package.json
{
"name": "aws-kms-did-sign",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1",
},
"author": "",
"license": "MIT",
"devDependencies": {
"dotenv": "^9.0.2"
},
"dependencies": {
"@tradetrust-tt/tradetrust": "^6.9.4",
"ethers-aws-kms-signer": "^1.1.0"
}
}
// .env
KMS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<Access key ID>
KMS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<Secret access key>
KMS_REGION=<Region>
KMS_KEY_ID=<Key ID>
Update the .env variables, npm i then node index.js. You should get a signed document.json that can be verified by DID method.